Introduction
Did you know only 2 out of 10 employees are happy about how their work performance is managed?
Well, it’s not just employees.
Even organizations are catching on that the old-school annual performance reviews don’t really cut it. They’re a headache for both managers and employees – time-consuming, frustrating, and yielding no actual results.
Lately, performance management has taken center stage in the business world. It has become an on-the-go necessary ritual everywhere, and understandably so.
Today’s workforce, particularly millennials, is not interested in annual report cards. They want something practical, something that can actually help their career progress. From their leaders, they seek clear expectations, accountability, a rich purpose, and especially ongoing feedback and coaching.
In this blog post, we will dive into the effective execution of performance management. Discover how it can help you foster a positive work culture that meets employee expectations and yields tangible business ROIs.
What is performance management?
Performance management is an ongoing process focused on evaluating and improving the performance of individuals, teams, and, ultimately, the entire organization. It is not just about annual appraisals; performance management goes beyond that.
Ideally, businesses set clear goals and metrics, from big-picture objectives down to what frontline employees do every day. Managers keep an eye on these metrics and frequently discuss progress with their teams. Positive performance gets rewarded, and necessary adjustments are made if things are not up to par.
Result: It creates a shared understanding of objectives and a leadership approach, ensuring those goals are met.
However, this ideal picture barely touches the tip of the iceberg. Before we dive into how things actually look in practice, let’s first understand the value effective performance management brings to the table.
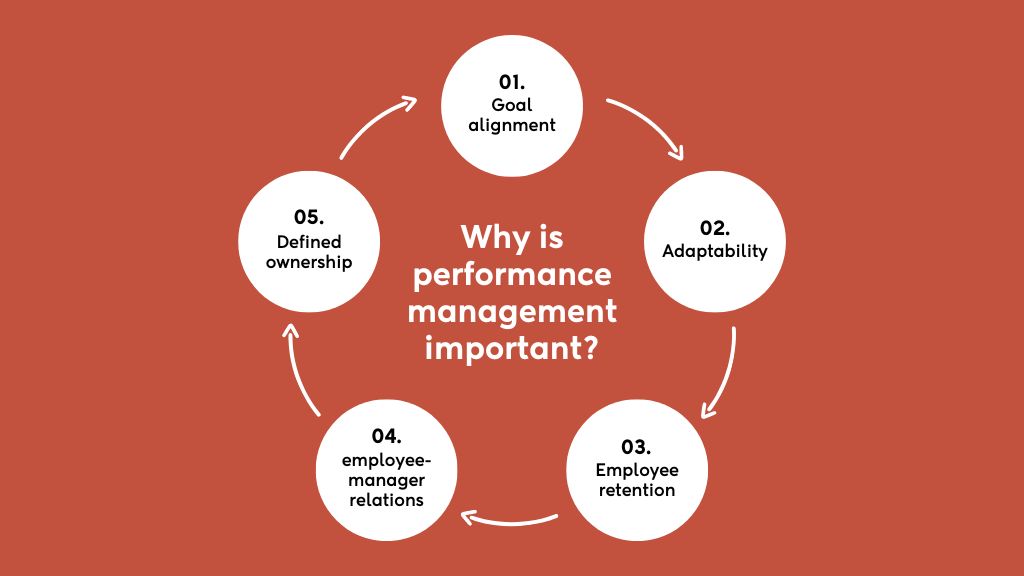
Why is performance management important?
Performance management directly impacts the chances of achieving business objectives. It’s no coincidence that companies like Google, Adobe, and Netflix, which often make headlines for revamping their performance evaluation systems, consistently outperform in the competitive landscape.
On the other hand, a study by Gallup revealed that poor management estimates to cost up to $1.24 trillion per year in the United States alone.
Your teams, through their performance, shape the future trajectory of the company. Simply put, the success of the organization is directly linked to the performance of its employees. An effective performance management system ensures that employees’ efforts are contributing positively to the company’s competitiveness and financial success.
Here are some of the most commonly observed benefits of effective performance management:
- Goal alignment: Everyone wants to see how their work fits into the big picture. Performance management, with its frequent feedback loop, aligns individual efforts with the broader strategic goals of the organization. Knowing their contribution matters motivates employees to give their best.
- Adaptability: In today’s fast-paced business world, adaptability is crucial. Well-executed performance management becomes the key to helping teams stay agile and responsive to market shifts, tech advancements, and internal changes. Regular assessments enable organizations to tweak goals and strategies on the fly.
- Employee retention: The concept of a ‘job for life’ is history. Your top talent seeks an environment that values continuous learning and growth. A fair performance management system not only offers room for improvement but also boosts employee retention by showcasing that the organization cares about their personal growth, too.
- Improved employee-manager relations: Past annual reviews felt like judgment day, disliked by both managers and employees. Performance management breaks this cycle, providing room for open communication. Employees feel empowered to share their thoughts, providing managers with insights to enhance processes based on employee preferences.
- Defined ownership and accountability: Regular feedback in performance management ensures each team member knows their role, receives recognition, and takes ownership of their part in collective success. Knowing your position in the field brings out the best play in you.
However, the performance management system in many companies is sluggish, shaky, or downright broken. At best, these organizations are missing out on added productivity. At worst, changes in technology, markets, or competition leave them unable to respond effectively.
Read more: What is Quite Quitting? 13 Ways to Prevent it in the Workplace
7 Performance management tips for managers

Performance management can be a tricky beast. In addition to the above techniques, here are some of the tips for managers to effectively manage the performance of their teams
1. Start small and then scale
Don’t go all in at once. Start with a new performance management system in a single department before company-wide implementation. Learn from the first go. Gather key learnings and refine the system based on feedback before expanding to other departments.
2. Leverage good technology for efficiency
Ditch the spreadsheets. Use intuitive tools that simplify goal tracking. Begin with a department where mid-year changes are likely to test the technology in a real-world scenario.
3. Promote regular check-ins
Make the continuous performance evaluation your ritual. Instead of those big end-of-year sit-downs, make regular assessments of work and individuals a priority.
4. Keep things simple
Start with basic goals and add on to them. Utilize modern performance management tools with pre-built goal templates for efficiency. Emphasize the human aspect by recognizing employees’ shared desire to excel in their roles.
5. Prioritize career development
Careers matter, big time! Keep an eye on things like upskilling and plan succession to retain your top talents. Align development with business goals and redefine how your team members can grow in a changing job market.
6. Listen and Adapt
Get feedback from everyone in the organization. Use metrics to identify issues early, ensuring a smooth process that benefits businesses and individuals alike.
7. Enhance Internal Mobility
Optimize internal mobility by involving all stakeholders simultaneously. Use numbers to convince any doubting managers. Internal moves are gold and have proven benefits over new hires.
6 Techniques for effective performance management

In performance management, the primary focus is aligning it with business outcomes. Doing annual or bi-annual performance appraisals is not the right way to go about it. Performance management is an ever-evolving process that can differ from one company to another. Here are some of the most prominent techniques that can be employed for effectively measuring and analyzing performance.
1. 360-degree feedback
The 360-degree feedback technique is valuable for managers to comprehensively assess employees across various dimensions. This approach employs multi-rater scales to gauge employee performance. Rather than relying solely on a supervisor’s perspective, it involves evaluation from multiple internal stakeholders, encompassing the employees themselves, managers, peers, subordinates, and individuals in close working relationships.
What makes this technique increasingly popular in performance management is its inclusivity and diverse input sources. The evaluation process is overseen by an administrator, who may be an internal member of the organization or an external professional well-versed in performance appraisal and employee management.
One notable advantage of this approach is its ability to offer insights into how each staff member perceives and evaluates your performance. This 360-degree view ensures a more holistic understanding, fostering a comprehensive and nuanced assessment of an individual’s contributions within the workplace.
Also Read: Learn how to master the art of giving feedback
2. Management by objectives (MBO)
Mostly prevalent in modern development approaches, MBO is a performance management technique that provides a framework for superiors and subordinates to decide the objectives together.
In MBO, goal setting is the initial step. Managers and employees work together to define objectives aligned with the SMART criteria (specific, measurable, achievable, relevant, and time-bound).
Unlike traditional top-down approaches, MBO encourages participatory decision-making. Managers and employees regularly meet to assess progress, discuss challenges, and make necessary adjustments. This ongoing dialogue ensures continuous feedback and identifies areas for improvement.
Success in MBO is gauged by the extent to which employees achieve their predetermined objectives. Performance appraisal is result-oriented, focusing on outcomes and accomplishments rather than mere activities.
3. Performance reviews
Performance reviews involve managers setting up clear milestones or standards, even ethical ones, to judge performance. This means defining what’s important and specifying expectations, often overlooked due to managerial uncertainties or changes in leadership.
Performance reviews cover key aspects of employees’ professional lives, including pay, job assignments, and behaviors.
Effective reviews require analyzing the causes behind an individual’s performance issues and distinguishing between deficiencies in motivation or ability. This guides action plans, like providing training, exploring motivational incentives, or considering alternative roles.
The review conversation should be a two-way transfer of information, encouraging dialogue. Asking the employee to respond promotes understanding and explores differing interpretations of events.
4. Agile performance management (Highly recommended)
Agile performance management is one of the best approaches to managing performance in the modern world. It directly targets the stagnant nature of traditional performance management practices and addresses the need to be adaptive in today’s changing environments.
The key idea is “Shorter the period of priorities, better the chance to achieve them.”
The process involves regular check-ins, typically on a monthly or weekly basis, once realistic Objectives and Key Results (OKRs) are set. This encourages frequent open communication, builds meaningful relationships, and addresses issues proactively, avoiding the pitfalls of traditional methods, such as vagueness and biases.
In agile organizations, teams work autonomously with a clear focus on output, following strategic priorities rather than detailed instructions. Quarterly business reviews (QBR) ensure alignment, utilizing dynamic objectives that adapt to changing priorities. This bottom-up approach enhances engagement and commitment as individuals play a role in defining their goals.
Agile performance management is future-oriented, process-driven, and well-suited for the modern enterprise, making it more effective than traditional methods. A general marker of successful implementation of agile performance management is “Work should not feel like work.”
5. Key Performance Indicators (KPIs)
Key Performance Indicators (KPIs) are one of the most essential tools for managing performance. They offer measurable metrics to evaluate organizational processes and individual effectiveness.
Chosen based on relevance to business or specific goals, KPIs offer quantifiable measurements for tracking progress, identifying trends, and making data-driven decisions. Whether assessing financial performance, customer satisfaction, or operational efficiency, KPIs simplify performance evaluation.
These metrics are critical in continuous improvement, allowing organizations to pinpoint strengths and weaknesses, adapt strategies, and enhance overall effectiveness. This iterative process is essential for adapting to a dynamic business environment.
6. Balance scorecards
Managers often face a tough choice between financial outcomes and operational measures, like cycle time, when evaluating performance. A Balanced Scorecard is a strategic tool used to resolve this dilemma.
It incorporates financial measures reflecting past actions and pairs them with operational measures across customer satisfaction, internal processes, and the organization’s innovation and improvement activities – the very drivers of future financial performance. The Balanced Scorecard provides managers with a holistic view of business performance, answering four key questions:
- How do customers see the business? (external perspective)
- Where does our organization need to improve? (internal perspective)
- Can we keep improving and creating value? (innovation and learning perspective)
- How do we look to shareholders? (financial perspective)
This strategic framework ensures a balanced approach to performance evaluation. Thereby leading to an in-depth understanding of how well individual efforts are aligning with overall business objectives.
Typical performance management process
No matter the technique you choose for performance measurement, the process follows a set sequence: planning, monitoring, reviewing, and rewarding. These steps are crucial whether you’re checking in on employee performance daily, monthly, or annually. Here’s a short breakdown of these steps.
- Planning: Defining and setting goals
In the planning phase of performance management, the focus is on establishing and aligning individual goals with the company’s overarching objectives. This step is akin to charting the course – clarifying what needs to be achieved and ensuring everyone is on the same page.
- Monitoring: Periodic check-ins
The monitoring stage is where the action unfolds with regular check-ins. Here, bosses and employees engage in ongoing discussions about progress, address challenges, and identify the necessary support. It’s akin to having a supportive coach guiding you through the game, ensuring you stay on track and overcome obstacles.
- Reviewing: Evaluating progress
As the cycle progresses, the reviewing stage comes into play. This involves a thorough evaluation of the progress made against the set goals. It’s a reflective phase where achievements are acknowledged and areas for improvement are identified.
- Rewarding: Recognizing and reinforcing
The final phase, rewarding, is about recognizing and reinforcing positive outcomes. This could involve various forms of recognition, incentives, or feedback to acknowledge a job well done. It’s the culmination of the performance management process, providing closure to one cycle while preparing for the next.
Applying this process for the evaluation of staff groups reflects the transparency and fairness of the performance evaluation process. The real benefits of this process come from the structured approach to managing performance at an organization. It eliminates any ambiguity that comes with traditional methods.
Furthermore, it enables managers to make informed decisions about resource allocation, training needs, and recognition programs based on a comprehensive and objective analysis of team performance.
Conclusion
Companies with effective performance management systems tend to outperform others in competitive environments. Unlike traditional performance evaluation methods that prescribe actions, effective systems focus on understanding and improving individual team members’ performance. As a manager, investing ample time in this process helps align their efforts to the best with company objectives.
It empowers you to act as a mentor, guiding your team members toward realizing their full potential. Furthermore, it allows you to identify and address any performance gaps promptly, ensuring that the team operates at its optimal capacity.
Related article
Building High-Performing Teams: The Definitive Guide
FAQs
What are the 5 elements of performance management?
The key components include goal setting, continuous monitoring, feedback and coaching, performance appraisal, and employee development.
What is the main function of performance management?
The primary function of performance management is to enhance employee performance, development, and productivity by aligning individual goals with organizational objectives. It serves as a strategic tool to optimize workforce efficiency and contribute to overall business success.
Why is performance management important?
Performance management is crucial as it improves employee engagement and motivation, aligns individual and organizational goals, facilitates effective communication and feedback, identifies and addresses performance gaps, and supports employee development, fostering a culture of continuous improvement.


















No Comments